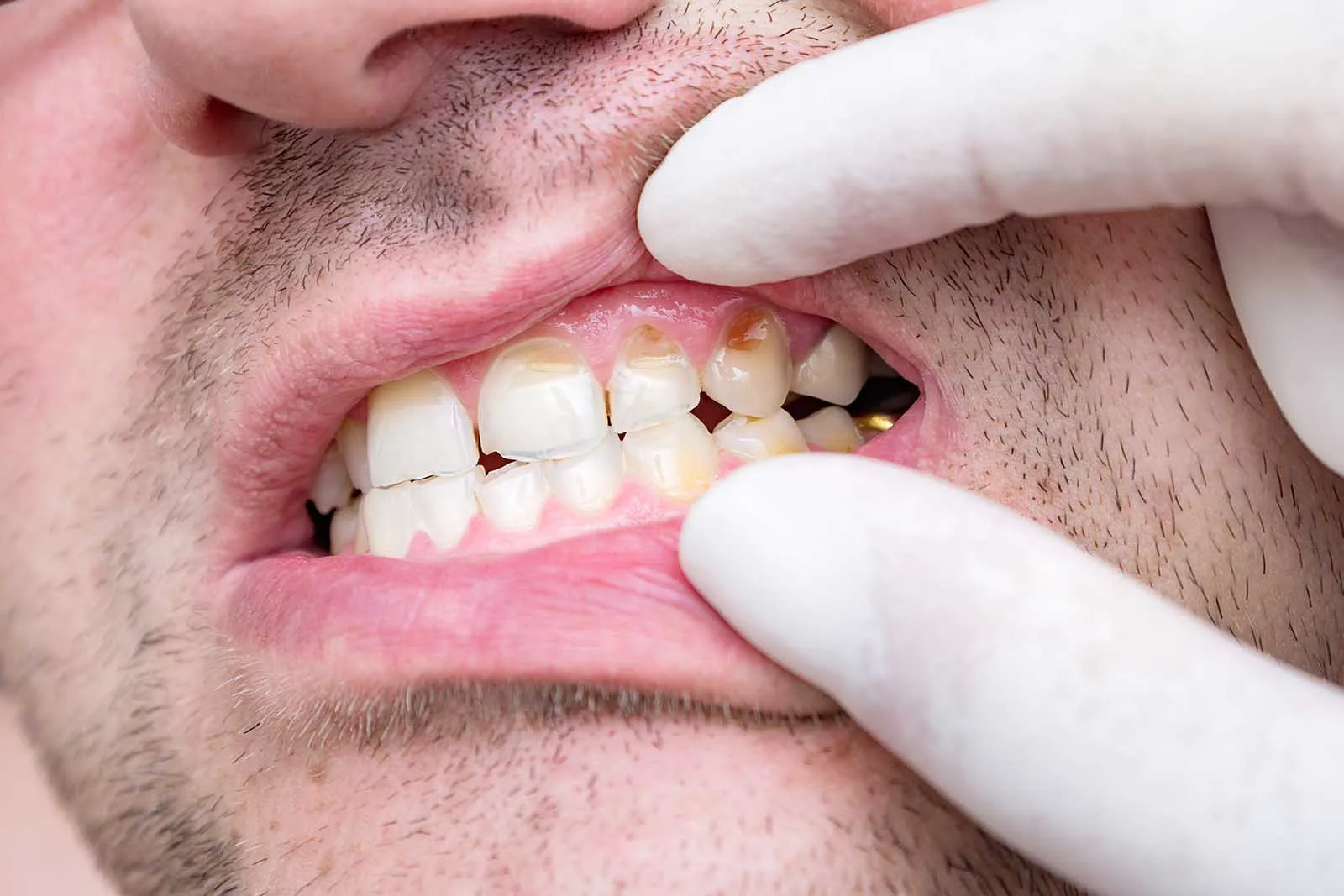
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition where the enamel layer of the teeth fails to develop normally. It usually occurs at birth or during childhood. Here are some essential facts about hypoplastic teeth:
What Are Hypoplastic Teeth?
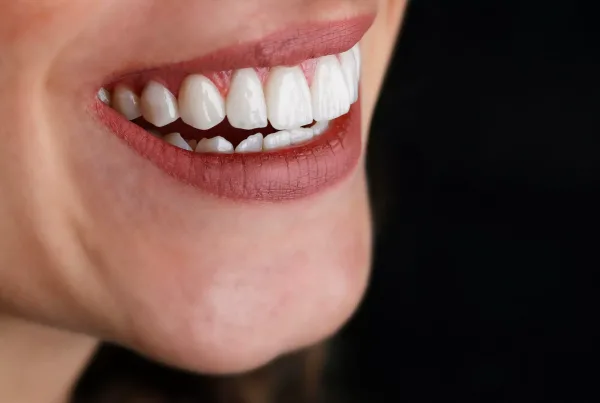
Hypoplastic teeth occur when the enamel is underdeveloped or missing, affecting the teeth’s durability and appearance. This condition typically appears during birth or childhood and manifests as noticeable spots or pits on the teeth.
Causes of Hypoplastic Teeth
Factors that may contribute to hypoplastic teeth include low birth weight, premature birth, smoking or poor nutrition during pregnancy, vitamin D deficiency, and specific genetic syndromes.
Symptoms of Hypoplastic Teeth
The signs of hypoplastic teeth are often visible changes on the teeth, such as:
- Color Changes: White or brown spots may appear on the teeth.
- Pits or Cracks: Due to insufficient enamel, pits or cracks may form, which are noticeable on the tooth surface.
- Shape Abnormalities: Deviations from the normal shape of the teeth, such as irregularities at the tips or edges, may occur.
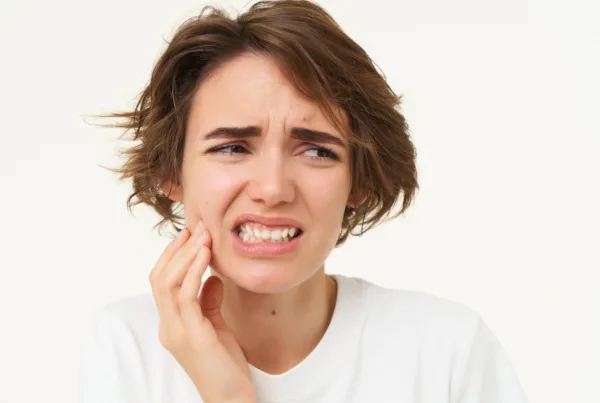
- Sensitivity: Hypoplastic teeth, due to their lack of enamel, can be more sensitive to hot or cold beverages or during brushing.
- Other Symptoms: Hypoplastic teeth may be more prone to cavities because the enamel layer is thinner or weaker.
If you or a loved one experiences these symptoms, consult a dentist.
Causes of Hypoplastic Teeth
Hypoplastic teeth can result from various factors, such as:
- Low Birth Weight and Premature Birth: These conditions can affect the normal development of teeth.
- Effects During Pregnancy: Poor nutrition, smoking, or alcohol consumption during pregnancy can adversely affect the baby’s tooth development.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic syndromes or diseases like Usher syndrome or Seckel syndrome can cause hypoplastic teeth.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Nutritional deficiencies during fetal development or childhood, especially vitamin D deficiency, can hinder healthy enamel development.
- Other Health Issues: Systemic diseases or health problems, including hormonal disorders and metabolic diseases, can impact tooth development.
Other Health Issues Caused by Hypoplastic Teeth
Hypoplastic teeth not only affect appearance but can also be indicative of other conditions, such as:
- Usher Syndrome: A genetic disorder characterized by hearing loss and progressive vision impairment, often with hypoplastic teeth as a symptom.
- Seckel Syndrome: Characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, facial bone abnormalities, and often hypoplastic teeth.
- Other Genetic Syndromes: Conditions like Down syndrome, Treacher Collins syndrome, and Kabuki syndrome may include hypoplastic teeth as symptoms.
Dental Problems Caused by Hypoplastic Teeth
Hypoplastic teeth can lead to various dental issues, including:
- Difficulty Cleaning Plaque: Pits or cracks can increase plaque buildup and make cleaning difficult, leading to cavities and gum disease.
- Sensitivity During Brushing: The thin enamel can cause heightened sensitivity, potentially discouraging regular brushing.
- Erosion by Acidic Foods: Hypoplastic teeth are more vulnerable to erosion by acidic foods and drinks.
- Low Durability: Hypoplastic teeth are less durable due to weak or missing enamel.
- Cavity Formation: Cavities can develop more quickly due to the weaker enamel.
Treatment Methods for Hypoplastic Teeth
Treatment for hypoplastic teeth depends on the severity and the patient’s needs and preferences. A dentist can determine the most suitable treatment option. Common treatments include:
- Veneers: Thin porcelain or composite layers are applied to the front surface of teeth to improve their appearance.
- Bleaching: Whitening treatments to reduce stains or discoloration.
- Composite Fillings: Resin materials are applied to the teeth to improve shape and structure.
- Enameloplasty: Applying unique enamel material to the tooth surface to rebuild the enamel layer.
- Orthodontic Treatments: Correcting shape or alignment issues to improve aesthetics and function.
Regular dental care and check-ups are essential for individuals with hypoplastic teeth to manage symptoms and maintain dental health.