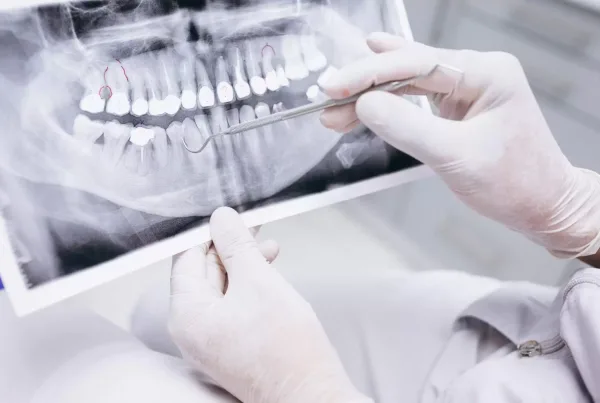
Aging can cause changes in various aspects of our body, one of which is the appearance of our teeth. Many of us notice that our teeth seem larger as we grow older.
Gum Recession is a common occurrence during the aging process. As gum recession progresses, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making the teeth appear larger. Therefore, most of the changes in the appearance of teeth during aging are related to gum recession.
What is the Gum Recession?
Usually, gums cover the teeth and support the roots. However, if the gums recede due to various factors, the roots of the teeth become exposed, making the teeth appear longer and larger. This condition is known as gum recession.
Causes of Gum Recession
Gum recession can result from a combination of factors, including:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate and ineffective teeth cleaning can lead to plaque buildup and gum recession.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of gum infection and contributes to gum recession.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal shifts, especially during pregnancy or menopause, can increase gum sensitivity and cause recession.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may be genetically prone to gum recession.
- Medical Conditions: Various health conditions can weaken the immune system and affect gum health, contributing to gum recession.
Gum recession can also be caused by trauma to the teeth, poorly fitted dental prosthetics, or other factors. Combining one or more of these factors often leads to this condition.
Symptoms of Gum Recession
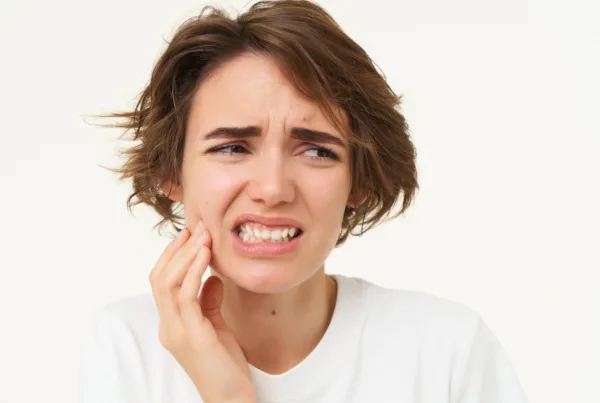
Gum recession may initially go unnoticed as it progresses slowly. However, several signs can indicate its presence:
- Tooth Sensitivity: The exposed roots of the teeth can cause sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Teeth Appearing Longer and Larger: As the gums recede, the teeth’s roots become more visible, making the teeth appear longer and larger.
- Gum Bleeding: Weakened gums may bleed, especially during brushing or flossing.
- Increasing Gaps Between Teeth: Recession can widen the gaps between teeth, weakening their connection and causing teeth to shift.
- Inflammation and Redness in Gums: Gum recession can lead to inflammation and redness, indicating unhealthy gums.
- Loose Teeth: As gum recession progresses, the supportive tissues weaken, leading to tooth mobility.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s recommended to consult a dentist. Early detection allows for more effective treatment, helping to preserve your dental health.
Advanced Gum Diseases
Gum diseases refer to infections and inflammation in the gums that can cause significant damage as they progress. Some advanced gum diseases include:
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gums, characterized by redness, swelling, bleeding, and sensitivity. If caught early, gingivitis can be reversed.
- Periodontitis: If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a deeper inflammation of the gums that can lead to gum recession, jawbone damage, and tooth loss.
- Periodontal Abscesses: As periodontitis advances, bacteria can accumulate in the gum pockets, causing infections and abscesses filled with pus.
- Necrotizing Gum Diseases: Rare and severe conditions in which gum tissue dies, requiring urgent medical attention.
- Peri-implantitis: Inflammation around dental implants, leading to implant failure and tooth loss.
These advanced gum diseases can harm gum health and lead to tooth loss. Early and effective treatment can halt their progression.
Causes of Advanced Gum Diseases
Advanced gum diseases often develop due to the neglect of minor symptoms. Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum inflammation, can evolve into more severe conditions like periodontitis if untreated. Poor dental hygiene and hormonal changes can increase the risk of these diseases. Chronic stress and medical conditions like diabetes can also impair the immune system, making it easier for gum diseases to develop.
Maintaining Healthy Gums and Teeth
To ensure healthy gums and teeth, regularly follow these steps:
- Brush Your Teeth Regularly: Brush your teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss Daily: Use dental floss or an interdental brush to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Use Mouthwash: An antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Limit sugary and starchy foods, and consume plenty of fruits, vegetables, proteins, and dairy products.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both increase the risk of gum disease.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist every six months to detect and treat gum issues early.
When Does Tooth Growth Stop?
Tooth development occurs in two stages. The first phase involves baby teeth, which emerge during infancy and are replaced by permanent teeth between ages 6 and 13. Humans typically have 28 permanent teeth in adulthood, though wisdom teeth may increase the total to 32.
Do Teeth Keep Growing?
While some animals, like rodents, have continuously growing teeth, human teeth do not grow continuously. However, aging can cause changes such as gum recession, making teeth appear larger, but this is not actual growth, just a change in appearance.