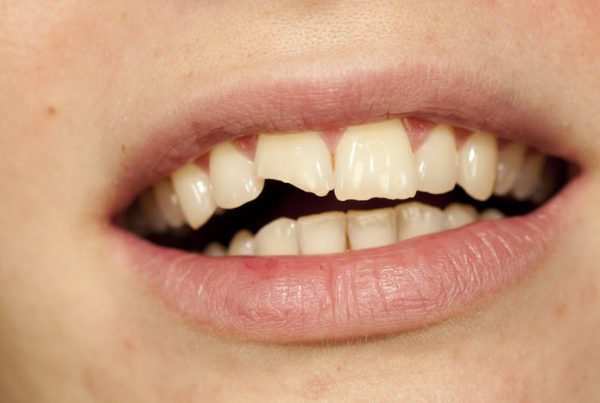
Malocclusions of the mouth refer to conditions that arise due to misalignment of the jaw and teeth. One such condition is known as an “overbite.” An overbite is characterized by the upper teeth being positioned too far forward compared to the lower teeth, which means the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth more than usual.
Types of Malocclusions of the Mouth
Malocclusions of the mouth refer to various conditions arising from jaw and teeth misalignment. These situations stem from a mismatch in the relationship between the upper and lower jaw. The main types of malocclusions are as follows:
- Overbite (Vertical Difference Between Upper and Lower Jaw): An overbite occurs when the upper teeth are positioned too far forward than the lower teeth. This means the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth more than usual. An overbite can result from structural differences in teeth and jaw growth.
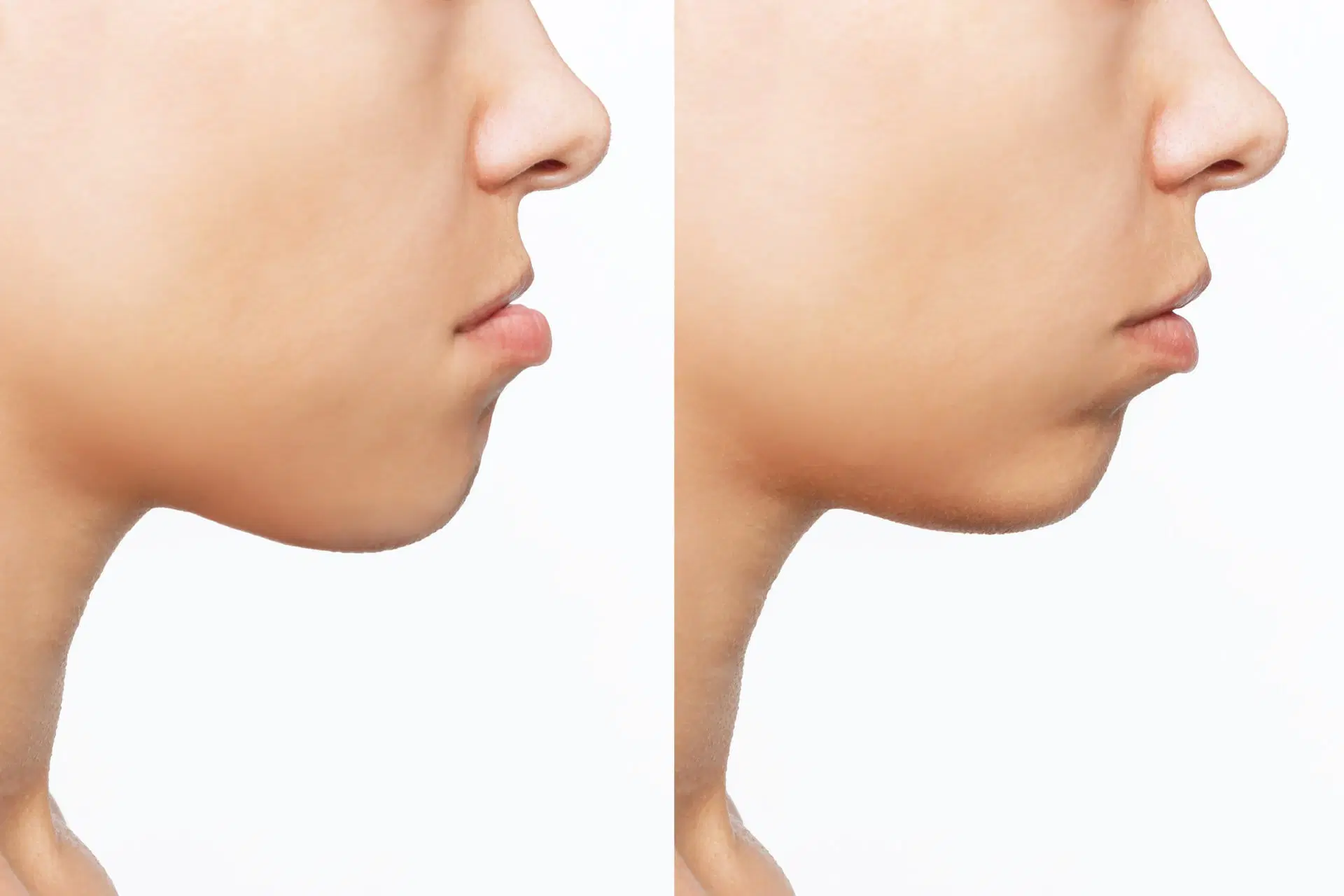
- Underbite (The Reverse of the Vertical Difference Between the Upper and Lower Jaw): An underbite refers to the lower teeth being positioned too far forward than the upper teeth. This condition indicates a jaw misalignment, where the lower teeth are in front of the upper teeth. An underbite typically arises from jaw structural disorders or genetic factors.
- Overjet (Protrusion of Upper Teeth Relative to Lower Teeth): An overjet occurs when the upper jaw teeth extend too far horizontally beyond the lower jaw. This situation means the distance between the upper and lower jaw teeth is more significant than usual. Genetic factors and structural jaw anomalies cause Overjet.
Each of these malocclusions may require different symptoms and treatment methods.
Why Does Overbite Occur?
Various factors can cause the development of an overbite:
- Genetic Factors: Mouth malocclusions are often associated with genetic predisposition. If you have a family history of overbite, you may also be prone to this condition.
- Jaw Structure and Growth: Jaw structure and growth play a significant role in the development of an overbite. Dimensional or positional differences between the upper and lower jaw can lead to an overbite.
- Incorrect Use of Pacifiers or Bottles: Incorrect use of pacifiers or bottles during infancy can cause teeth to misalign, thereby developing an overbite.
- Thumb-Sucking Habit: Prolonged thumb-sucking during childhood can push the upper teeth towards the lower teeth, leading to the development of an overbite.
Additionally, factors such as jaw trauma, missing teeth, edentulism, or incorrect tooth eruption can influence the formation of an overbite.
Symptoms and Possible Complications of Overbite
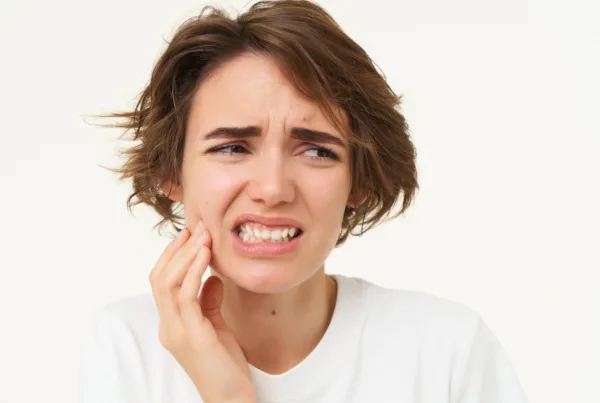
An overbite often becomes apparent when the upper teeth are positioned too far forward in relation to the lower teeth. This condition may make the upper teeth more prominent when you smile. An overbite can cause stress and tension in the jaw joints, leading to jaw pain and discomfort. It can also hinder normal tongue movement.
Jaw stress and tension caused by an overbite can lead to headaches. If you have teeth-grinding or clenching habits, headaches may occur more frequently. An overbite can prevent the proper alignment of the teeth, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum problems.
An overbite can cause pain and tension around the jaw joints, negatively affecting quality of life. It increases the risk of developing tooth decay, gum issues, and other oral health problems due to improper tooth positioning.
It may also make proper chewing of food difficult, potentially causing digestive problems. An overbite can negatively affect an individual’s self-confidence, leading to psychological issues, especially in those who are self-conscious about aesthetics. Untreated overbite can lead to more severe health problems and adversely affect quality of life.
Treatment for Overbite
Treatment varies depending on the severity of the overbite, the patient’s age, and overall health. The primary goal of overbite treatment is to ensure proper alignment of the jaw and teeth, preventing potential complications. Here are some methods used in overbite treatment:
- Orthodontic Treatment: Orthodontic treatment (braces) is the most commonly used method for correcting an overbite. Brackets and wires are regularly applied to align the teeth properly. This method is effective in cases of mild or moderate overbite.
- Use of Plates and Appliances: Special plates or appliances can sometimes correct an overbite. These devices help gently shift the teeth and jaws into the correct position, aiding in the correction of an overbite.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, especially when the overbite is severe. Surgical procedures may involve reshaping the jawbones or adjusting the jaw joints.
Overbite treatment addresses aesthetic concerns and improves jaw and dental health. Starting overbite treatment early can be more effective, making it extremely important for children.
What Can Happen if Overbite is Left Untreated?
An overbite can cause stress and tension around the joints, leading to chronic jaw pain and headaches. The misalignment of teeth can increase the risk of tooth decay, gum problems, and other oral health issues. It can also lead to excessive wear and tear on the teeth.
Preventive Measures for Overbite at Home
Overbite is usually caused by problems with the teeth and jaw structure and often requires treatment. However, taking measures at home and in daily life can help prevent the progression of overbite and potential complications. Here are some preventive measures for overbite:
- Regular Dental and Oral Care: Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for protecting the health of teeth and gums. Brushing daily and using dental floss and mouthwash help clean plaque and food debris, thus preventing tooth decay.
- Promoting Dental Health Habits: Teaching children proper brushing and flossing habits is essential.
- Mouth and Jaw Exercises: In some cases, mouth and jaw exercises can help correct an overbite. These exercises can strengthen jaw muscles and support the proper positioning of teeth.
- Control of Bad Habits: Habits such as thumb-sucking, nail-biting, or other oral habits can contribute to developing an overbite. Controlling or preventing these habits can help stop the progression of an overbite.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Regular visits to the dentist are essential for early detection of problems in teeth and jaw structure and determining appropriate treatment options.
- Proper Nutrition Habits: A balanced diet and healthy eating habits can contribute to developing teeth and jaws. It is important to teach children to avoid hard or sticky foods.
- Reducing Stress and Tension: Habits such as teeth grinding or clenching related to stress and tension can contribute to the progression of an overbite. Techniques to reduce stress can help control these habits.
If symptoms of overbite are noticed or potential risk factors are present, consulting a dentist is advisable. An expert evaluation can help determine an appropriate treatment plan and prevent the progression of an overbite.