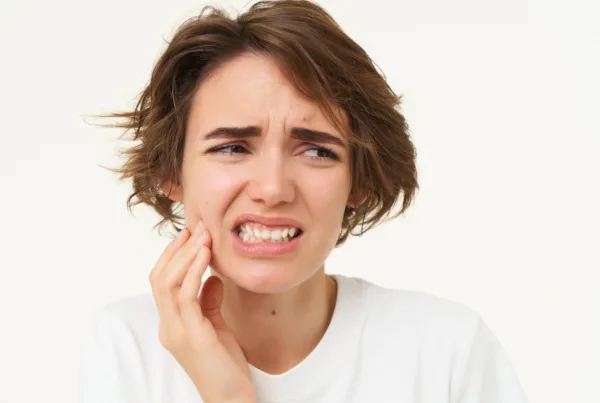
Gingival (gum) bleeding can be common during pregnancy and menstrual cycles, but it is not necessarily “normal.” While hormonal changes can contribute to increased sensitivity and inflammation of the gums, bleeding gums should not be ignored. It’s important to understand the reasons behind gingival bleeding during these periods and take steps to maintain good oral health.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, hormonal changes, particularly increased levels of progesterone, can lead to an exaggerated response of the gums to irritants such as plaque and bacteria. This condition is known as “pregnancy gingivitis.” Symptoms may include redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis can progress to more severe gum disease. Good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, are essential during pregnancy.
- Menstrual Cycles: Some women may experience mild gingival changes, including bleeding, during their menstrual cycles due to hormonal fluctuations. While this is generally temporary and not a cause for concern, it’s still important to maintain proper oral hygiene.
To address gingival bleeding during pregnancy and menstrual cycles:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Use a Gentle Technique: Avoid aggressive brushing and use a gentle, circular motion to clean your teeth and gums.
- Rinse with Antiseptic Mouthwash: Using an alcohol-free antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and prevent inflammation.
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health. Adequate vitamin C intake is especially important for gum tissue health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water helps flush away bacteria and food particles.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor your oral health and address any concerns.
If you experience persistent or severe gingival bleeding, consult a dentist or periodontist (gum specialist). They can evaluate your condition, provide appropriate treatment if needed, and offer guidance on maintaining good oral health during pregnancy and menstrual cycles.
Remember, while some gingival changes may occur due to hormonal fluctuations, bleeding gums should not be ignored, as they can be a sign of underlying gum disease that requires professional attention and care.